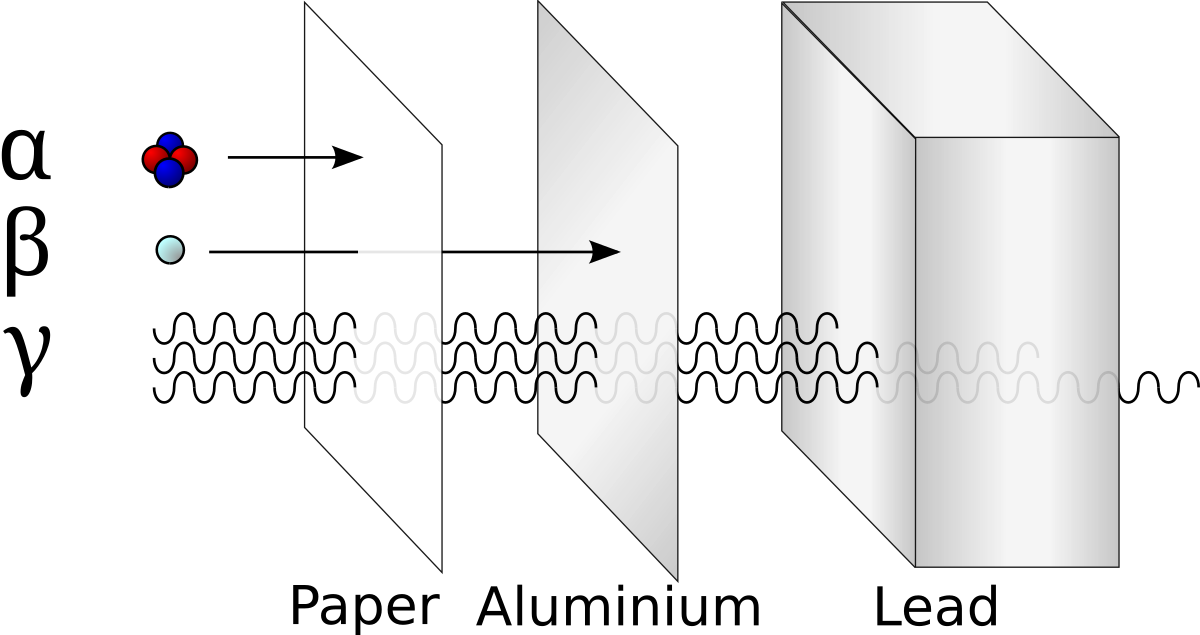
One rad is 100 ergsgram in other words 100 ergs of energy absorbed by one gram of a given body tissue. Introduction of radioactive materials into the body for measurements of organ function from the detection of radioactive emissions nonimaging studies do not require a gamma camera to determine radio isotope uptake and often use biological samples or probes to determine organ function radioactive iodine is often used and can be swallowed as. Radiation doses are often calculated in the units of rad short for radiation absorbeddose. The dose of absorbed radiation multiplied by the hazard factor of the type of radiation. Introduction of radioactive materials into the body for the study of distribution and fate of certain substances by the detection of radioactive emissions measurement of absorption of radioactive emissions from an external source. Beta particles are electrons emitted from an atom.
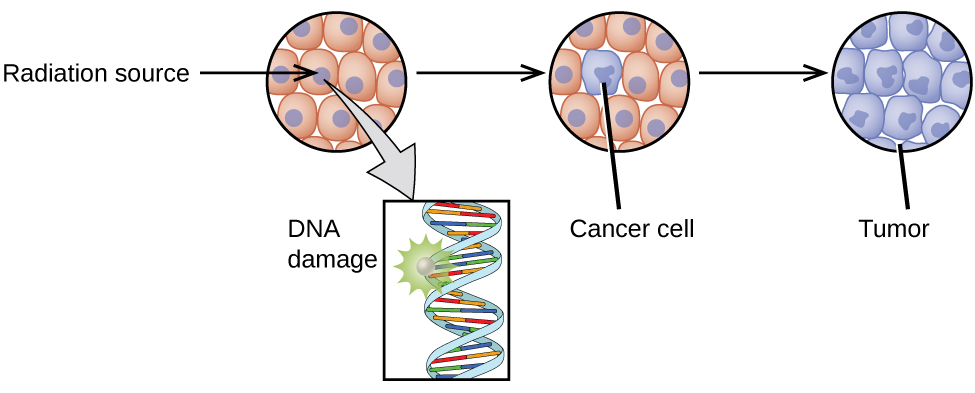
It can directly kill cells or it can. The activity and the mass of a radioactive body diminish at the same rate the mass has been expressed in terms of the number of atoms in order for it to be placed on the same scale. Inside the body they can kill nearby cells. Outside the body alpha particles wont even go through the outer layer of skin. As radioactive material decays or breaks down the energy released into the environment has two ways of harming a body that is exposed to it higley said. The radioactive body chosen is iodine 123 and the initial activity of 1 millicurie is equivalent to that of a thyroid scintigraphy.
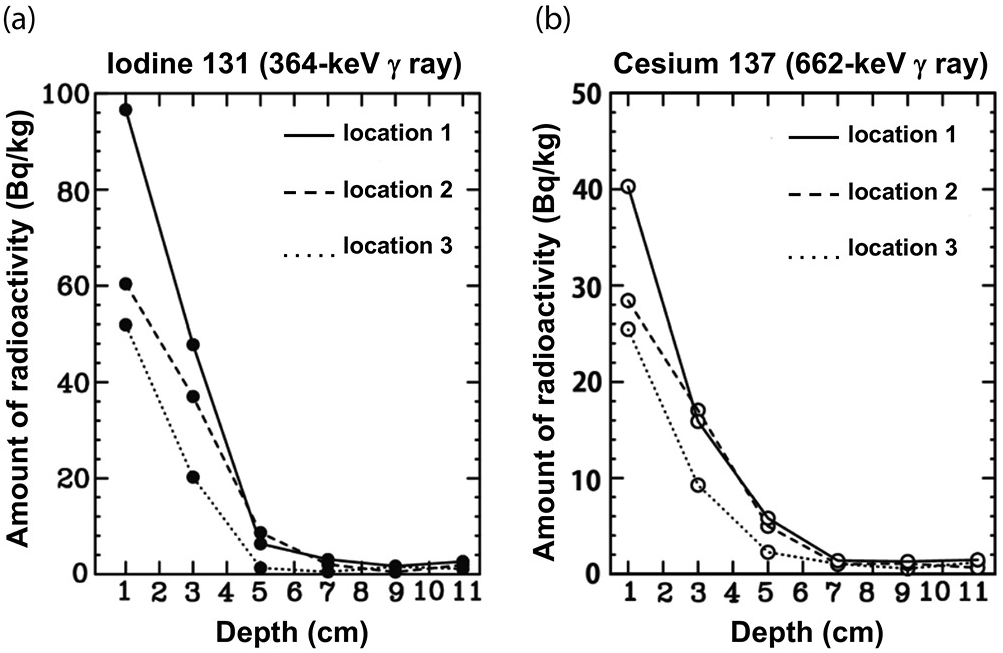
Such contamination presents a hazard because of the radioactive decay of the. Occur when the body is exposed to radioactive material outside the body primarily a concern for gamma radiation internal doses occur from exposure to radioactive material taken into the body by inhalation or ingestion this is a concern for alpha and beta radiation as well as gamma radiation. To derive the body content of 226 ra some measurement or assumption must be made to determine the retention of 222 rn the first decay product of 226 ra and the parent of 214 pb 214 bi by the body. Dose is generally not uniform over the body. A radioactive substance can be selectively taken up by different organs or tissue. Biological influence of radiation during.
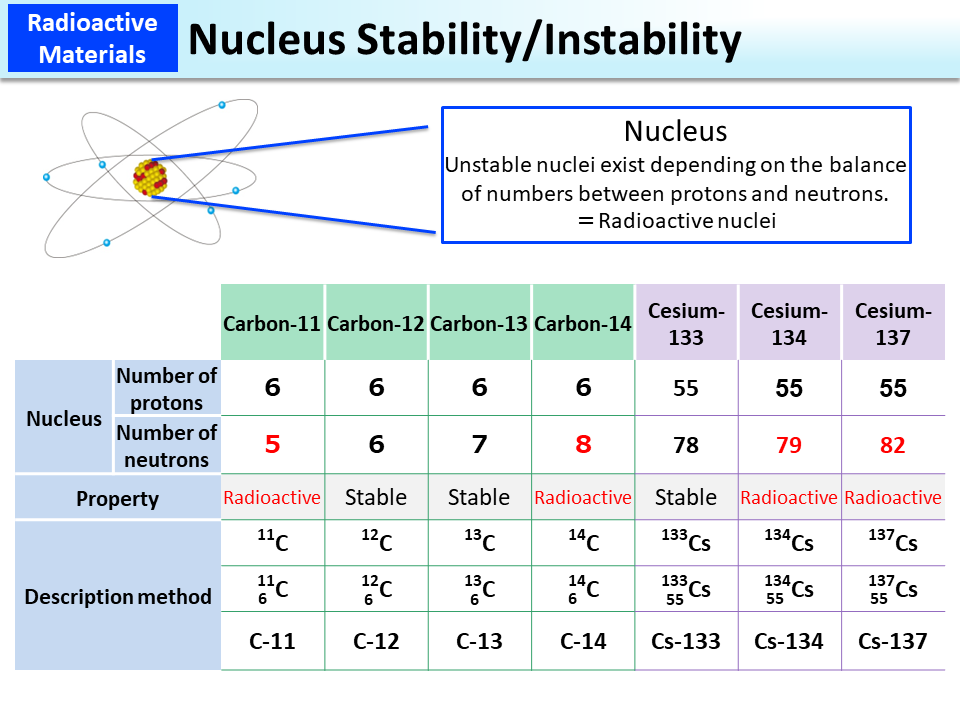
Radioactive contamination also called radiological contamination is the deposition of or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids liquids or gases including the human body where their presence is unintended or undesirable from the international atomic energy agency iaea definition. The sum of equivalent doses for all parts of the body taking into account the effect on each organ. From these gamma ray emissions whole body counting can measure the body content of 214 pb 214 bi. Examples of radioactive materials that give off alpha particles are polonium 210 radon 222 radium 226 and americium 241.


/GettyImages-151867495-56a798ab3df78cf772977296.jpg)